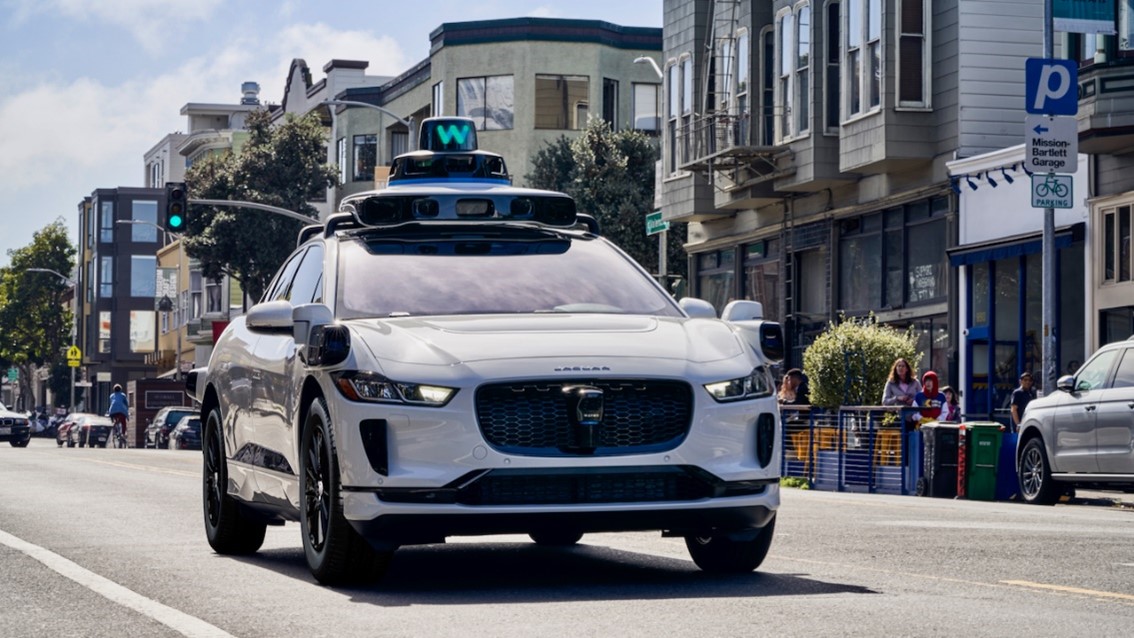
Imagine a car that can see up to three football fields away, make split-second decisions using AI, and can drive you to your favorite dinner place for $1 to $2 per mile. It is a reality, the Waymo Company has achieved this using a technology called LiDAR.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure distances and create 3D models of the Earth’s surface. In LiDAR, laser light is sent from a source, a transmitter, and reflected from objects in the scene. The reflected light is detected by the system receiver and the time of flight (TOF) is used to develop a distance map of the objects in the scene.
The prototype of LiDAR was developed in 1961 by the Hughes Aircraft Company, it was first widely used in 1980. Now, LiDAR is used all over the world in many different applications including drones, self-driving cars, archeology, and iPhones.
LiDAR can be used in a variety of applications. Archeologists use LiDAR to find and study historical sites, literally uncovering history. A group of archeologists and historians are using LiDAR to discover more hidden chambers at the Chichen Itza site created by the Mayans.
Another application for LiDAR is drones. The DJIAir 3S currently uses a combination of LiDAR, cameras, and an infrared sensor to achieve omnidirectional obstacle sensing which means it can detect anything around it. Even your iPhone uses LiDAR to create 3D models, improve camera quality, and enable night mode portraits.However, if the lighting is bad, cameras struggle. This is where LiDAR comes in. No matter the visibility, time of day, or weather, LiDAR still works.
For more information: